24 min read
The Beginner's Guide to MPC Wallets
Welcome to "The Beginner's Guide to MPC Wallets", your essential starting point to explore the transformative potential of Multi-Party Computation (MPC) wallets. As digital security and privacy become increasingly vital in our connected world, MPC wallets are revolutionizing how we manage secure transactions and protect sensitive keys.
This guide is designed to simplify the complexities of MPC wallets, making it accessible whether you're just starting out or looking to deepen your understanding. Along the way, we’ll uncover how these innovative wallets are shaping the future of secure digital interactions.
Here’s what we’ll explore together:
- The Basics: A clear introduction to MPC and how it powers next-generation wallet solutions.
- Real-World Impact: Practical examples that showcase how MPC wallets are transforming industries.
- Benefits and Challenges: A balanced look at what makes MPC wallets a game-changer—and what to watch out for.
- The Road Ahead: Emerging trends and innovations that promise to push MPC wallets even further.
Whether you’re a tech enthusiast, a blockchain advocate, or someone seeking a secure wallet solution, this guide will provide the knowledge you need to confidently navigate the world of MPC wallets. Let’s dive in!
What is MPC?
At its core, Multi-Party Computation (MPC) is a subfield of cryptography that allows multiple parties to jointly compute a function over their inputs while keeping those inputs private. The essence of MPC is to enable this collaborative computation without any single party having access to the others' data. MPC emerged from the field of cryptography in the 1980s. It was initially a theoretical concept, but over the years, it has evolved significantly, driven by both advances in computational power and a growing need for data privacy.
Basic Principles of MPC
Secret Sharing
Secret sharing is a cryptographic protocol that plays a pivotal role in ensuring data privacy and security. It involves dividing a secret, such as a cryptographic key or a piece of sensitive information, into multiple parts, known as shares. These shares are then distributed among a group of participants. The key aspect of secret sharing is that the original secret can only be reconstructed when a sufficient number of these shares are combined together. This threshold is predetermined and ensures that no single participant can access the full secret on their own.
Here are 2 of the most common secret sharing schemes in use today:
Shamir's Secret Sharing Scheme
Developed by Adi Shamir in 1979, this is one of the most widely used secret sharing schemes. It is based on polynomial interpolation in finite fields. In Shamir's scheme, the secret is transformed into a polynomial of degree d, where d is one less than the number of shares required to reconstruct the secret (this is also known as the threshold). For instance, if the threshold is 3, the polynomial will be of degree 2. Each share is a point on this polynomial. To reconstruct the original secret, a minimum number of shares equal to the threshold is required. These shares are used to interpolate the polynomial, and the secret is the constant term of this polynomial.
Think of Shamir's method as a jigsaw puzzle. You have a picture (which is your secret) and you break it into many puzzle pieces. You give each friend a piece of the puzzle. Only when enough friends (the number you decide, like 3 or 4) come together and join their pieces, can they see the whole picture and find out the secret. If they have fewer pieces than needed, they can't see the full picture, so they can't guess the secret.
Blakley's Secret Sharing Scheme
Proposed by George Blakley around the same time as Shamir's, this scheme is based on geometric properties. In Blakley's method, the secret is represented as a point in an n-dimensional space. Each share corresponds to a hyperplane in this space. The intersection of at least n such hyperplanes (where
n is the threshold) is a single point, which is the secret. Much like Shamir's method, unless the threshold number of hyperplanes (shares) is available, the secret cannot be determined. Blakley’s scheme is notable for its simplicity and the fact that it offers a different mathematical approach to secret sharing, rooted in geometric concepts.
Blakley's method is like having a treasure map. You draw lines on the map, and where enough lines cross, that's where the treasure (your secret) is hidden. You give each friend a different line to add to the map. Only when enough friends (again, a number you decide) come together and draw their lines on the map, will they find the crossing point where the treasure is hidden. If not enough friends come together, they won't find the crossing point and can't find the treasure.
Computational Trust
Computational trust refers to the reliance on mathematical algorithms and protocols to establish and verify trust in digital environments. Unlike traditional trust, which is often based on personal experiences and subjective judgment, computational trust is built upon objective, algorithmically driven processes.
In the context of blockchain technology, computational trust is exemplified by the use of cryptographic techniques and consensus algorithms. For instance, cryptographic methods like public and private key encryption ensure that transactions are secure and that identities are authenticated, thereby creating a trust layer over digital interactions. MPC itself is a cryptographic technique that distributes trust among multiple parties. No single party can compromise the computation or the privacy of the data.
Additionally, consensus mechanisms, such as Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS), further reinforce trust. These mechanisms allow a network of decentralized and often anonymous participants to agree on the validity of transactions without needing a central authority, thus creating a trustless environment where participants can engage securely based on the assurance provided by the computational processes themselves.
What is an MPC Wallet?
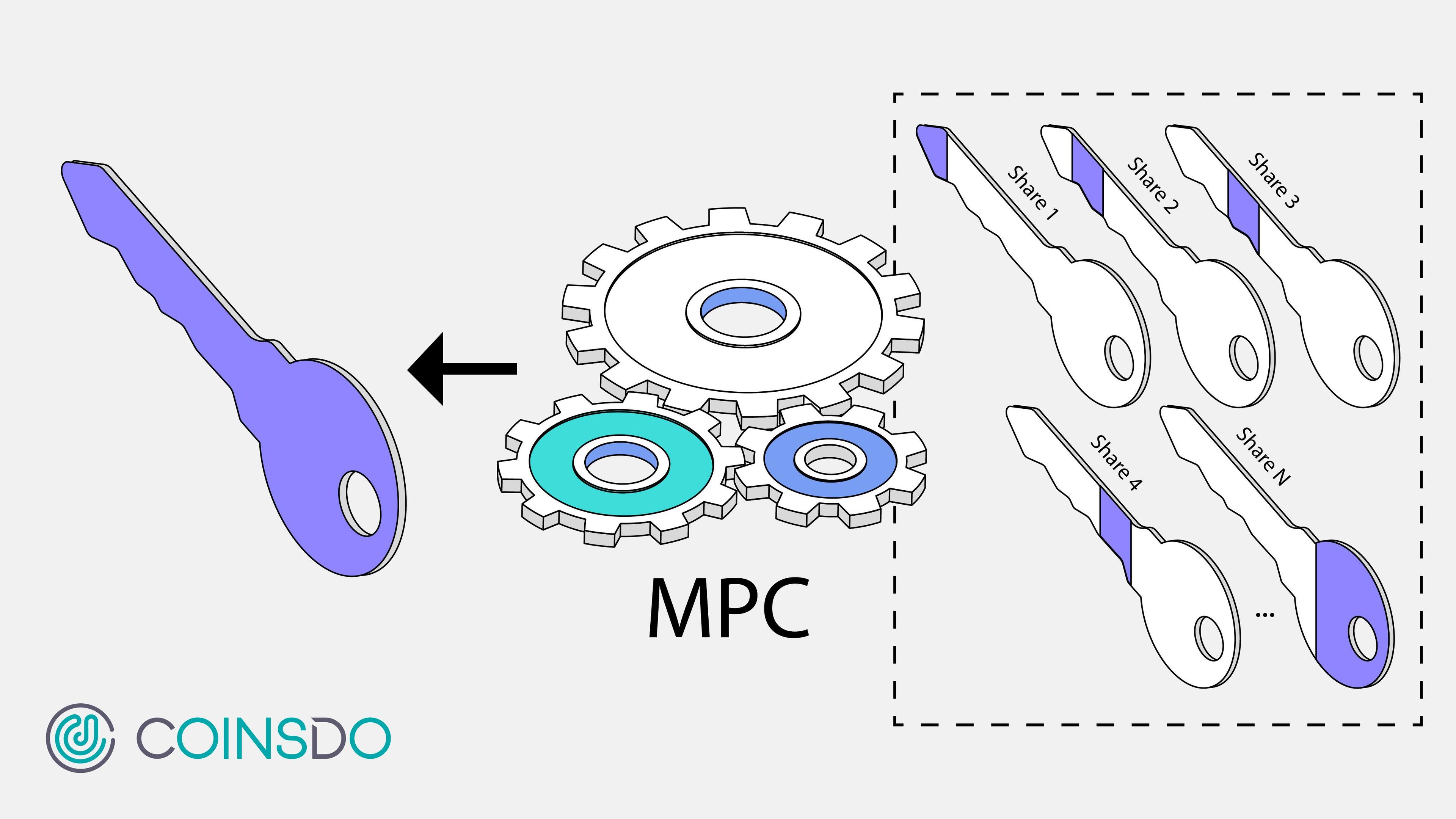
MPC wallets are built on the foundational principles of Multi-Party Computation (MPC) technology, leveraging its cryptographic capabilities to redefine digital asset security. Unlike traditional wallets that rely on a single private key, MPC wallets split the key into encrypted shares distributed across multiple devices or participants. These shares collaborate through MPC protocols to authorize transactions without ever reconstructing the entire key, ensuring enhanced protection against theft, loss, and unauthorized access. By utilizing MPC technology, these wallets offer a secure and flexible solution for managing digital assets in an increasingly interconnected world.
Witness MPC Wallets in Action
Imagine a company with multiple departments, such as Research, Marketing, and Operations, each managing its own budget. To ensure robust security and shared accountability in treasury operations, the company adopts a Multi-Party Computation (MPC) wallet for fund management. In this setup, the wallet's private key is divided into key shards using MPC technology, with each shard distributed to the heads of different departments.
When a department needs to initiate a transaction, at least two department heads must collaborate by using their key shards to authorize the transfer. This approach not only strengthens security—making it nearly impossible for unauthorized access even if one shard is compromised—but also promotes shared control and collective decision-making over company finances. The result is a wallet solution that fosters collaboration while streamlining operations.
For a more straightforward application, consider a group of three friends managing a shared cryptocurrency investment. Each friend holds a shard of the wallet’s private key, requiring any two of them to approve transactions. This ensures that no single individual can act unilaterally, offering a balance of security and trust while managing shared assets.
How MPC Works in Wallets
At the heart of MPC wallets lies a process grounded in advanced cryptographic principles. Here’s how the technology enables secure and private collaboration:
1. Input Gathering
Each participant contributes a private share of the key. In the context of wallets, these shares are created during the initial setup, with no single party ever holding the full private key.
2. Key Fragmentation
The private key is divided into encrypted shards using cryptographic techniques, akin to breaking a secret into incomprehensible pieces.
3. Distributed Key Shares
Each shard is distributed among the participants or devices, ensuring that no single entity can access or use the wallet independently.
4. Secure Computation
When a transaction is initiated, the participants use their key shards to perform cryptographic operations collaboratively, authorizing the transaction without ever reconstructing the full private key.
5. Final Authorization
The results of these computations are combined, allowing the transaction to proceed securely while preserving the privacy and security of the key fragments.
The Top Benefits of Using MPC Wallets
Multi-Party Computation (MPC) wallets are quickly gaining traction for their innovative approach to digital asset management. By leveraging advanced cryptographic techniques, MPC wallets offer a range of benefits that make them ideal for both individuals and businesses. Let’s break down the key advantages:
1. Enhanced Security
MPC wallets eliminate the traditional reliance on a single private key by splitting it into multiple encrypted shares. These shares are stored across different devices or parties, ensuring that no one entity has complete control. This approach reduces the risk of theft, phishing attacks, or unauthorized access, as an attacker would need to compromise multiple shares simultaneously.
2. Resilience Against Single Points of Failure
Traditional wallets are vulnerable to the loss or theft of private keys. With MPC wallets, the absence of a single key ensures that even if one share is compromised, the wallet remains secure.
3. Flexible Multi-Signature Functionality
MPC wallets support collaborative decision-making by requiring multiple participants to approve transactions.This feature is especially valuable for organizations managing corporate funds or requiring layered security for high-value transactions.
4. Seamless Cross-Platform Compatibility
MPC technology integrates smoothly with various platforms and devices, allowing users to access their wallets from smartphones, tablets, or desktops. This cross-platform flexibility makes MPC wallets highly adaptable to diverse use cases and user preferences.
5. Adaptable Authentication Methods
MPC wallets can incorporate advanced security protocols, including biometric verification, hardware tokens, and two-factor authentication. These additional layers of security enhance the wallet’s usability without compromising protection.
6. Non-Custodial and Custodial Options
Users can choose between non-custodial wallets, where they retain control of their assets, or custodial wallets, which offer managed services with MPC technology. This flexibility caters to individual preferences and business needs, making MPC wallets a versatile solution.
7. Simplified Recovery Mechanisms
Traditional wallets often leave users stranded if they lose their private key.
MPC wallets offer innovative recovery options by allowing lost key shares to be regenerated securely without exposing the entire wallet to risk.
8. Scalability for Enterprise Use Cases
MPC wallets are designed to handle complex transaction workflows, making them ideal for businesses managing multiple accounts or requiring multi-party approvals.
They also support integration with enterprise-grade tools and platforms, enabling seamless operations at scale.
The Key Challenges and Limitations of MPC Wallets
While Multi-Party Computation (MPC) wallets offer numerous benefits, they aren’t without their downsides. Understanding these challenges is crucial for determining whether MPC wallets are the right solution for your needs. Here are some of the key drawbacks to consider:
1. Increased Complexity
The advanced cryptographic processes behind MPC wallets can be difficult for non-technical users to understand. Setting up and managing an MPC wallet may require more steps and learning compared to traditional wallets, which could deter first-time users.
2. Dependence on Multiple Devices or Parties
Since MPC relies on splitting private keys into shares distributed across devices or parties, any failure in one component (e.g., a lost device or unresponsive party) could delay access or transactions.This setup can add logistical challenges, especially in emergencies where quick access to funds is needed.
3. Potential for Higher Costs
The infrastructure required to support MPC wallets, such as secure server environments and ongoing maintenance, may result in higher operational costs. Businesses adopting MPC solutions may need to invest in additional resources or expertise, which could increase implementation expenses.
4. Recovery Challenges in Extreme Scenarios
While MPC wallets offer innovative recovery mechanisms, recovering a wallet in the event of multiple share losses or unavailability of key stakeholders can still be complex and time-consuming.These challenges are amplified in cases of catastrophic failures involving multiple devices or users.
5. Limited Industry Support and Adoption
MPC technology is still relatively new, and not all platforms or service providers support it. Limited compatibility with certain blockchain networks or third-party tools may restrict the wallet’s usability for specific use cases.
6. Performance Concerns for High-Volume Users
MPC computations can introduce latency during transactions due to the added cryptographic operations required to verify and execute transfers. For high-frequency traders or businesses requiring rapid transactions, this delay may impact performance.
7. Reliance on Technology Providers
Many MPC wallets rely on third-party technology providers or proprietary algorithms, introducing concerns about vendor lock-in and long-term support. A provider’s discontinuation or security breach could pose risks to the wallet’s functionality and safety.
Unlocking the Potential of MPC Wallets: Diverse Use Cases in the Digital Economy
Multi-Party Computation (MPC) wallets are redefining how individuals and institutions manage digital assets. By leveraging cutting-edge cryptographic techniques, these wallets split private keys into encrypted shares, distributing them across devices or parties for enhanced security and flexibility. This innovative approach has spurred numerous use cases across industries, each demonstrating the unique value MPC wallets bring to the table. Here’s a closer look at where MPC wallets shine.
1. Enhanced Security for Cryptocurrency Management
MPC wallets are particularly beneficial for securing cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and other digital assets. Traditional wallets rely on a single private key, creating a single point of failure. MPC wallets eliminate this vulnerability by using sharded private keys, which are split into multiple parts and distributed among devices or users.
- Why It Matters: Even if one device is compromised, the entire key cannot be reconstructed, making it virtually impossible for hackers to access funds.
- Who Benefits: Individual investors, institutional crypto custodians, and exchanges looking to bolster security measures.
2. Seamless Management of Institutional Digital Assets
Institutional adoption of blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies has surged, creating a need for sophisticated wallet solutions. MPC wallets provide a scalable way for institutions to securely manage their digital assets while adhering to governance protocols.
- Why It Matters: Institutions often require multi-party authorization for transactions. MPC wallets enable multiple stakeholders to participate in decision-making without exposing the full private key.
- Who Benefits: Banks, asset management firms, and corporate treasuries conducting large or high-stakes transactions.
3. Secure Off-Chain Transactions
In scenarios where blockchain transactions are too costly or time-sensitive, MPC wallets support secure off-chain protocols. Off-chain transactions allow users to settle payments or agreements outside the blockchain while maintaining cryptographic security.
- Why It Matters: Off-chain solutions reduce transaction fees and latency, enabling quicker and more cost-effective digital interactions.
- Who Benefits: Payment processors, decentralized exchanges (DEXs), and platforms facilitating micropayments.
4. Collaborative Control in Multi-Device Environments
With the proliferation of connected devices, managing digital assets across multiple endpoints is increasingly complex. MPC wallets address this by distributing key shares among devices, ensuring no single device has full control.
- Why It Matters: If one device is lost or compromised, users can still access their funds through other devices, ensuring business continuity.
- Who Benefits: Organizations implementing bring-your-own-device (BYOD) policies, remote teams, and tech-savvy consumers.
5. Revolutionizing Digital Auctions
Digital auctions, especially those involving high-value items or NFTs (non-fungible tokens), benefit significantly from MPC wallets. These wallets provide secure, transparent, and multi-party verified bidding processes.
- Why It Matters: MPC ensures bidders’ private keys remain secure while verifying their participation, preventing fraud and unauthorized access during auctions.
- Who Benefits: Auction platforms, collectors, and participants in NFT and digital art markets.
6. Simplified Recovery for Sharded Private Keys
One of the most daunting aspects of traditional wallets is the irreversible loss of private keys. MPC wallets address this with secure recovery mechanisms that regenerate lost shares without compromising the overall key.
- Why It Matters: This is a game-changer for businesses and individuals managing large-scale assets, as it mitigates the risk of permanent loss.
- Who Benefits: Crypto custodians, enterprise wallet users, and individuals managing diverse digital portfolios.
7. Enhanced Protocol Flexibility
MPC wallets are highly adaptable to various blockchain protocols, making them suitable for diverse use cases. Whether supporting Ethereum’s smart contracts or Bitcoin’s simple transaction framework, MPC technology integrates seamlessly.
- Why It Matters: Businesses can deploy MPC wallets without being locked into specific protocols, ensuring long-term flexibility as blockchain standards evolve.
- Who Benefits: Developers, blockchain startups, and enterprises navigating multi-chain strategies.
8. Scalable Security for Decentralized Applications (DApps)
Decentralized applications (DApps) often require wallets that align with their distributed architecture. MPC wallets provide a perfect match by enabling secure multi-party interactions while maintaining user-friendly access.
- Why It Matters: DApps built on principles of decentralization can extend these values to their wallet solutions through MPC, ensuring both usability and security.
- Who Benefits: Developers and users of DeFi (decentralized finance) platforms, gaming DApps, and decentralized social networks.
9. Improved Governance for DAOs and Other Collectives
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) often involve multiple stakeholders participating in governance and treasury management. MPC wallets facilitate secure and democratic decision-making by requiring multi-party approval for transactions.
- Why It Matters: This eliminates the risk of unilateral control and promotes transparency, aligning with the core principles of decentralization.
- Who Benefits: DAOs, community-driven projects, and blockchain-based cooperatives.
10. Stronger Consumer Confidence Through Customizable Security
For end-users, MPC wallets offer customizable security settings, such as biometrics, two-factor authentication, and device-specific controls. This ensures a tailored experience without compromising the underlying security model.
- Why It Matters: Users can balance convenience with robust protection, making digital assets more accessible to a wider audience.
- Who Benefits: Retail users, small businesses, and startups onboarding non-technical customers.
Embracing the Future with Multi-Party Computation (MPC)
As we conclude this comprehensive exploration of Multi-Party Computation (MPC), it's clear that MPC is not just a cryptographic curiosity, but a pivotal technology shaping the future of data privacy and collaborative computation. From its theoretical underpinnings to its burgeoning array of applications, MPC stands as a testament to the incredible potential of combining mathematics, cryptography, and computer science to address some of the most pressing challenges of our digital age.
The journey through the various facets of MPC - its principles, applications, benefits, challenges, and future prospects - reveals a technology that is both powerful and nuanced. MPC offers a path to a world where collaborative data analysis and decision-making can occur without sacrificing individual privacy or data security. This is more than just a technological advancement; it's a step towards a more secure and privacy-conscious society.
If you're in the market for an MPC wallet, download CoinWallet here (Android) or here (iOS) today and discover why we're the preferred choice for institutions and enterprises.



